What Is an Absolute Encoder and How to Choose the Right One
What is an absolute encoder and why is it essential in modern automation? An absolute encoder is a precision sensor that provides unique position values, ensuring reliable motion control without needing a reset or homing sequence. Unlike incremental encoders, absolute encoders deliver continuous position feedback, making them ideal for applications in robotics, CNC machines, elevators, and industrial automation.
In this guide, we will explain what an absolute encoder is, how it works, the key differences from incremental encoders, and most importantly, how to choose the right absolute encoder for your specific needs. By understanding its benefits, types, and applications, you can make smarter decisions and enhance efficiency in your projects.
What Is an Absolute Encoder? Definition and Basics
An absolute encoder is a type of position sensor that provides unique digital values for every shaft angle, delivering precise and reliable feedback without requiring a homing sequence. Unlike incremental encoders that only track relative movement, absolute encoders store exact position data, even after power loss.
This makes them essential in automation, robotics, CNC machinery, and industrial equipment where accuracy and repeatability are critical. Absolute encoders are available in optical and magnetic designs, offering different levels of resolution and durability to match various applications. By providing true absolute position information, they ensure stability, efficiency, and seamless integration in modern motion control systems.
How Does an Absolute Encoder Work?
An absolute encoder works by assigning a unique digital code to every shaft position, ensuring precise and repeatable feedback without the need for homing. Unlike incremental encoders that only track relative movement, an absolute encoder stores position data even after power loss, making it ideal for automation, robotics, and CNC machinery.
Depending on the design, optical absolute encoders use light patterns while magnetic absolute encoders rely on magnetic fields to deliver accurate signals. This capability allows machines to maintain exact positioning, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency. Understanding how an absolute encoder works helps engineers select the right model for demanding industrial applications where accuracy and reliability are critical.
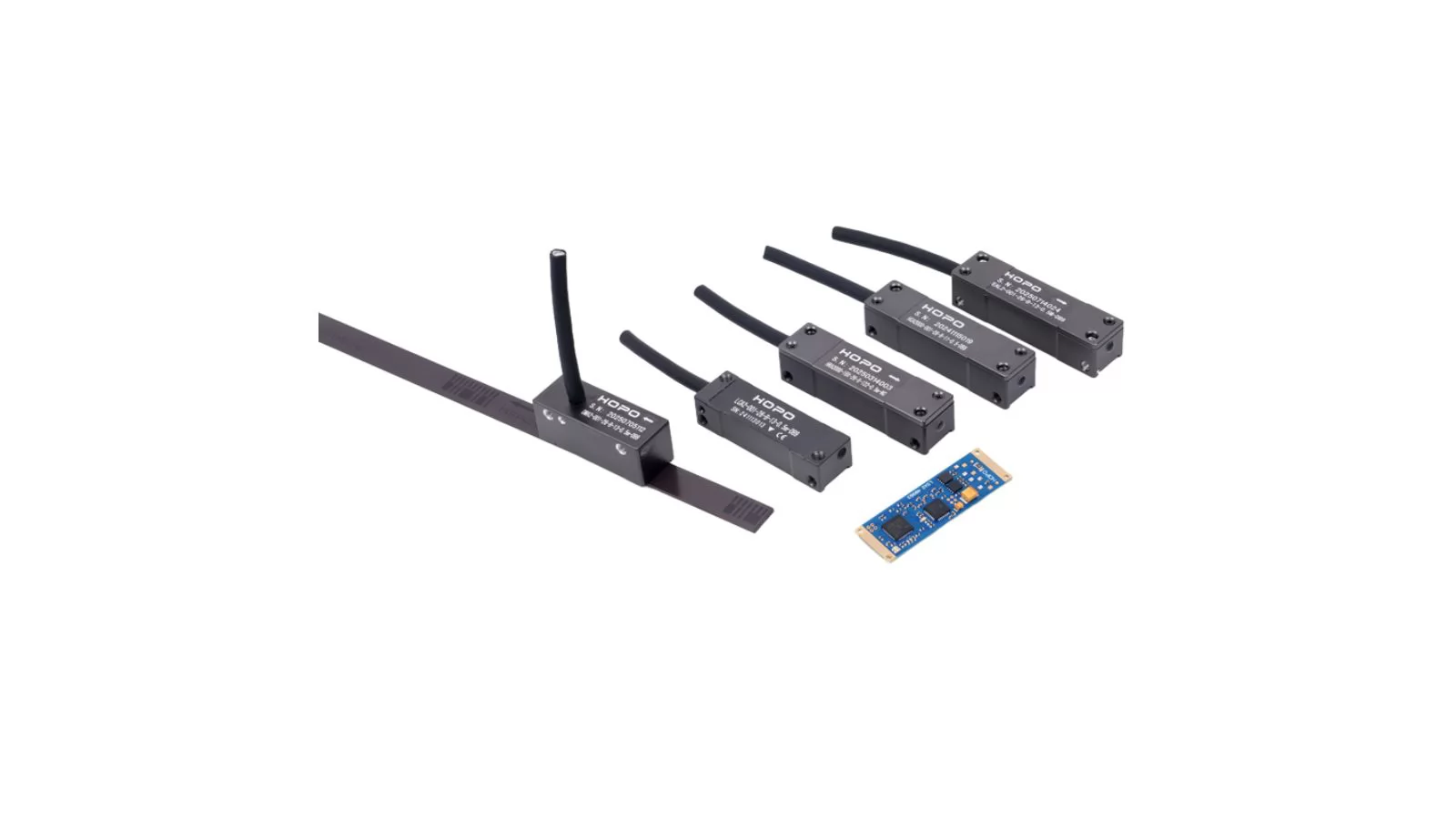

Absolute Encoder vs Incremental Encoder: Key Differences
When comparing an absolute encoder vs incremental encoder, the main difference lies in how position data is recorded. An absolute encoder provides unique position values, ensuring accurate feedback without needing homing on startup, making it ideal for robotics, CNC machines, and industrial automation.
In contrast, an incremental encoder delivers relative position changes, requiring reference points but offering a simpler and cost-effective solution. Choosing between absolute and incremental encoders depends on your application’s need for precision, reliability, and memory retention.
Types of Absolute Encoders Explained
- Single-Turn Absolute Encoder
A single-turn absolute encoder provides unique position values within one full rotation of the shaft. It is ideal for applications like CNC machines, robotics, and printing equipment where precise angular measurement is required. These encoders deliver accurate feedback without needing homing, making them reliable for short-range rotational tasks.
- Multi-Turn Absolute Encoder
A multi-turn absolute encoder can track position over multiple revolutions, making it suitable for complex automation systems and industrial machinery. Unlike single-turn types, it remembers the number of rotations even after power loss. This ensures long-term accuracy and reliability in applications such as elevators, wind turbines, and heavy-duty conveyors.
- Optical Absolute Encoder
Optical absolute encoders use light-based scanning technology to provide high-resolution feedback. They are often chosen for precision-demanding industries such as semiconductor production, medical devices, and laboratory automation. With excellent accuracy and stability, optical encoders are preferred in clean environments where fine detail and repeatability are critical.
- Magnetic Absolute Encoder
Magnetic absolute encoders rely on magnetic field sensing, making them highly durable in harsh environments with dust, vibration, or temperature fluctuations. They are commonly used in robotics, automotive systems, and outdoor industrial equipment. Their robust design ensures consistent performance where optical encoders might fail, offering a balance of accuracy and resilience.
Key Benefits of Absolute Encoders
- Precise Position Feedback Without Homing
An absolute encoder provides exact position data immediately after startup, eliminating the need for homing sequences. This ensures higher efficiency, minimizes setup time, and delivers consistent accuracy in automation and robotics applications.
- Reliable Operation in Harsh Environments
Unlike incremental encoders, absolute encoders can withstand dust, vibration, and temperature variations. Their robust design makes them ideal for heavy-duty industrial automation, CNC machinery, and outdoor equipment where reliability is critical.
- Enhanced Productivity and Reduced Downtime
By offering stable and repeatable motion control, an absolute encoder helps reduce machine downtime. This reliability translates to smoother operations, improved workflow, and lower maintenance costs in manufacturing and robotics industries.
- Long-Term Efficiency and Cost Savings
Although absolute encoders may have higher initial costs, their precision, durability, and reduced need for recalibration ensure long-term savings. They enhance system efficiency, providing a strong return on investment for industrial applications.

How to Choose the Right Absolute Encoder for Your Application
Selecting the right absolute encoder is crucial to achieving reliable motion control and long-term efficiency. Start by evaluating the required resolution and accuracy, as high-precision applications like robotics or CNC machines demand multi-turn absolute encoders. Consider the operating environment—optical encoders work best in clean conditions, while magnetic encoders excel in dust, vibration, or temperature extremes.
Check compatibility with your output interface (SSI, EtherCAT, or CANopen) to ensure seamless integration with existing systems. Balance cost vs performance to match your project budget without sacrificing reliability. By carefully analyzing these factors, you can choose the absolute encoder that guarantees accuracy, stability, and durability for your industrial application.
Conclusion: Invest in the Right Absolute Encoder
Choosing the right absolute encoder is critical for ensuring accurate motion control, reducing downtime, and improving long-term efficiency in robotics, CNC machines, and industrial automation. By comparing encoder types, understanding resolution and interface options, and matching them to your application, you can make the best investment for reliable performance. Absolute encoders offer unmatched precision and stability, making them a smarter choice over incremental models in demanding environments.
Ready to find the perfect solution for your project? Contact our team today to explore high-quality absolute encoders and get expert guidance tailored to your needs.
-
 Sep 04, 2025What Is a Rotary Encoder? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Sep 04, 2025What Is a Rotary Encoder? A Complete Beginner’s Guide -
 Sep 23, 2025Top 10 Optical Encoder Manufacturers in The World 2025
Sep 23, 2025Top 10 Optical Encoder Manufacturers in The World 2025 -
 Oct 22, 2025Top 10 Absolute Encoder Manufacturers in The World 2025
Oct 22, 2025Top 10 Absolute Encoder Manufacturers in The World 2025 -
 Sep 29, 2025Top 10 Linear Encoder Manufacturers in The World 2025
Sep 29, 2025Top 10 Linear Encoder Manufacturers in The World 2025